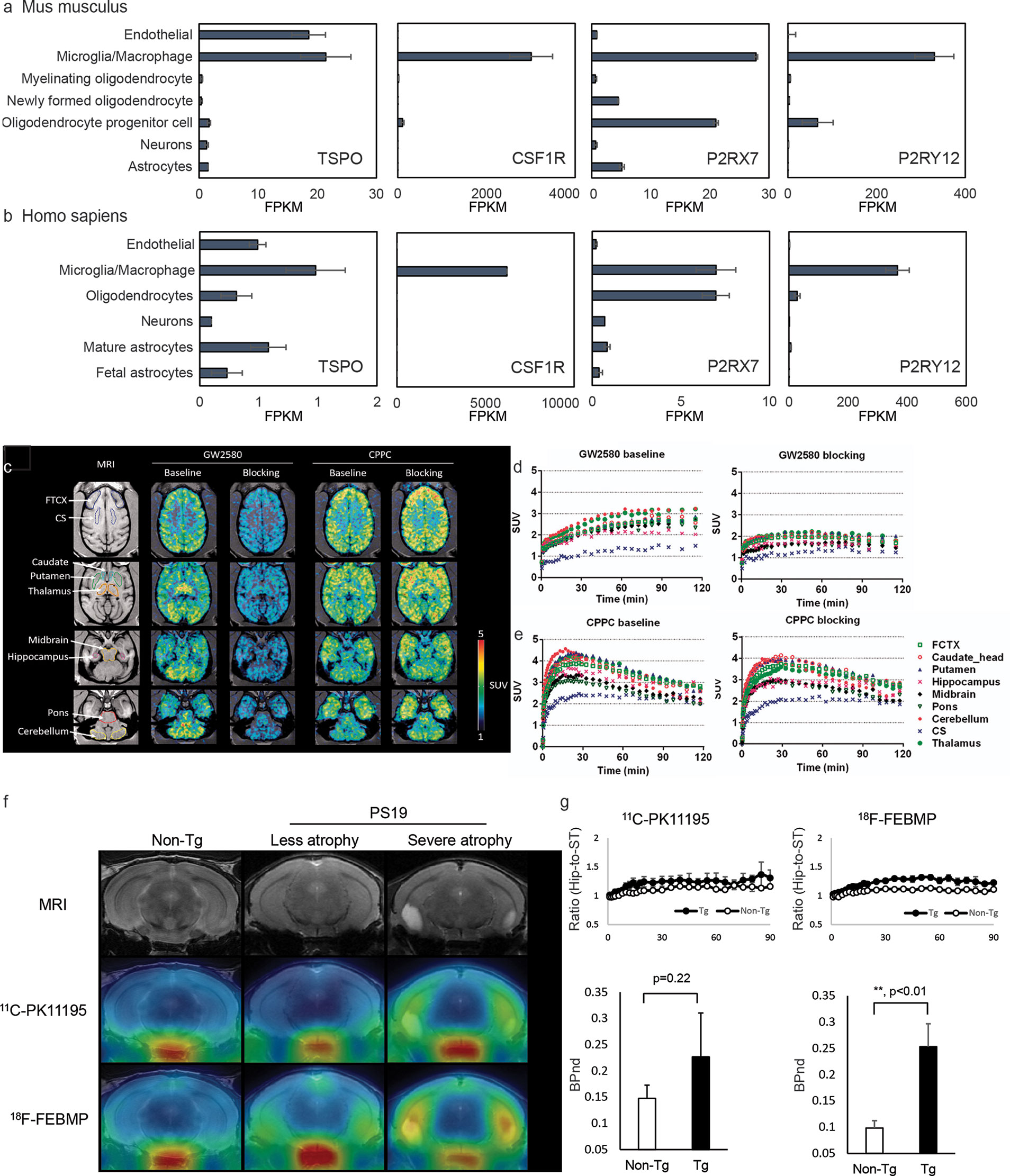
Lipopolysaccharide-induced c-Jun NH2-terminal Kinase Activation in Human Neutrophils - Journal of Biological Chemistry
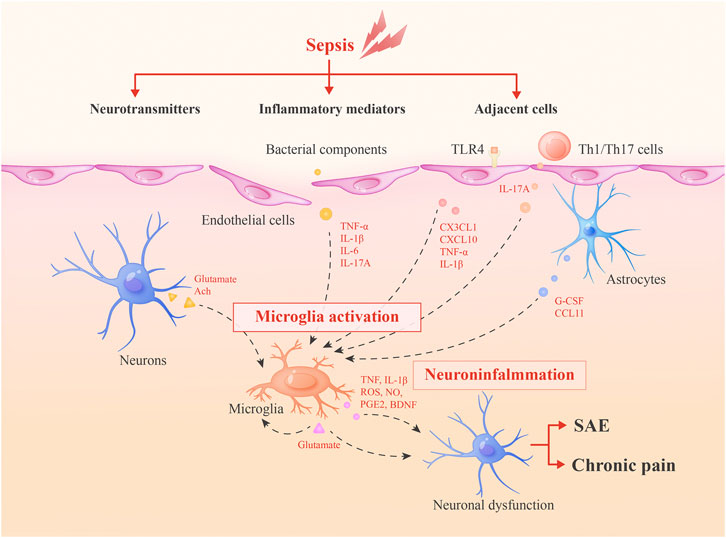
Frontiers | Microglia: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy and Sepsis-Associated Chronic Pain
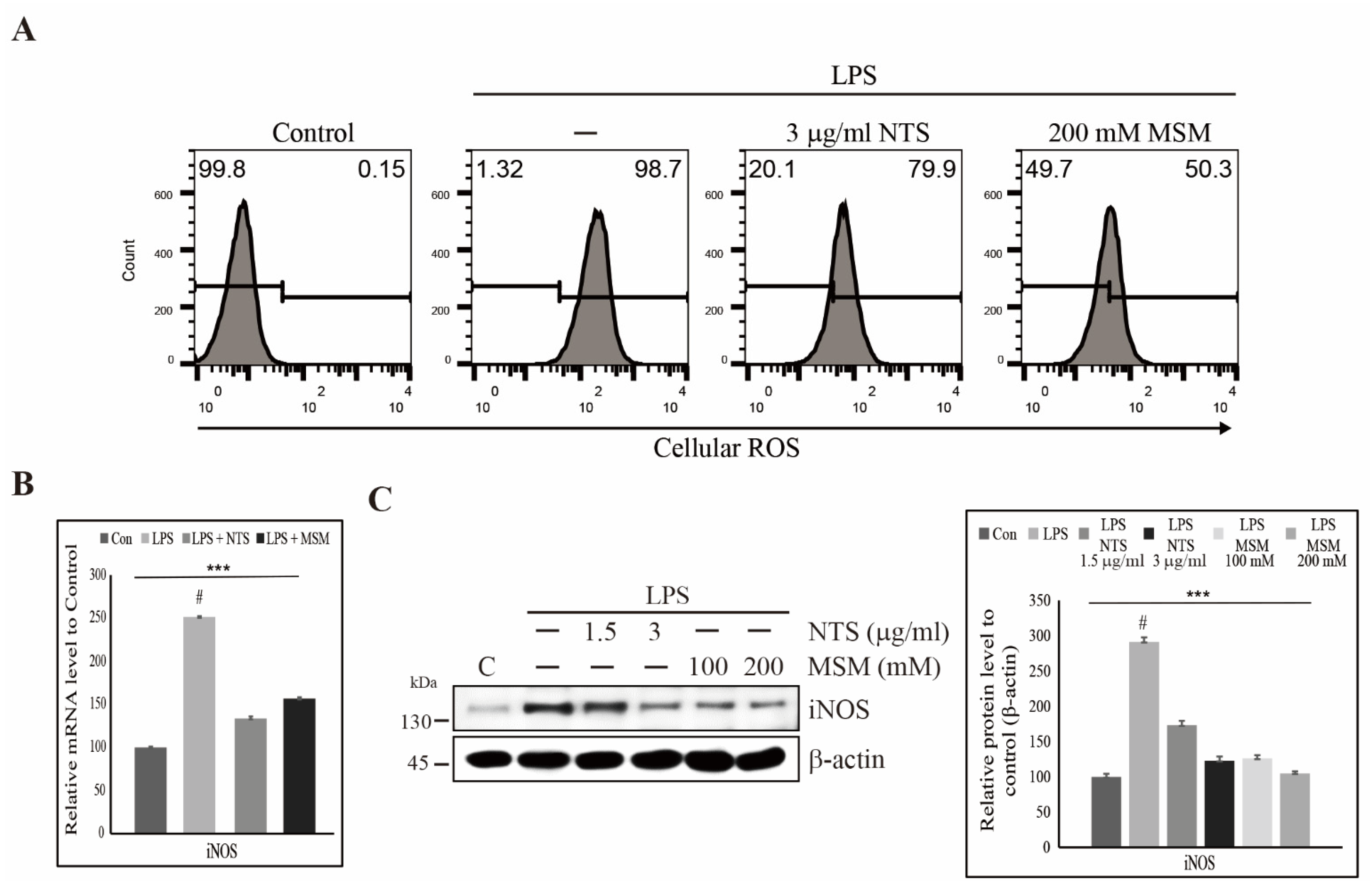
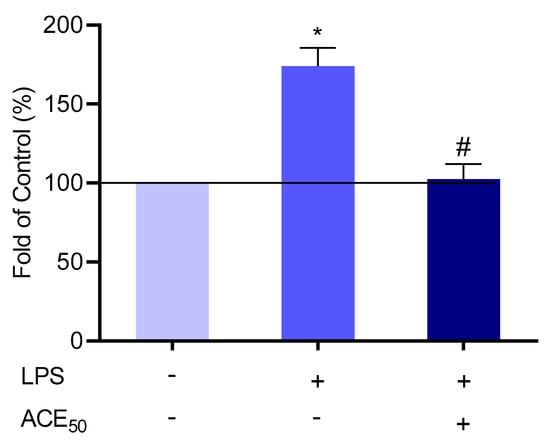
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts
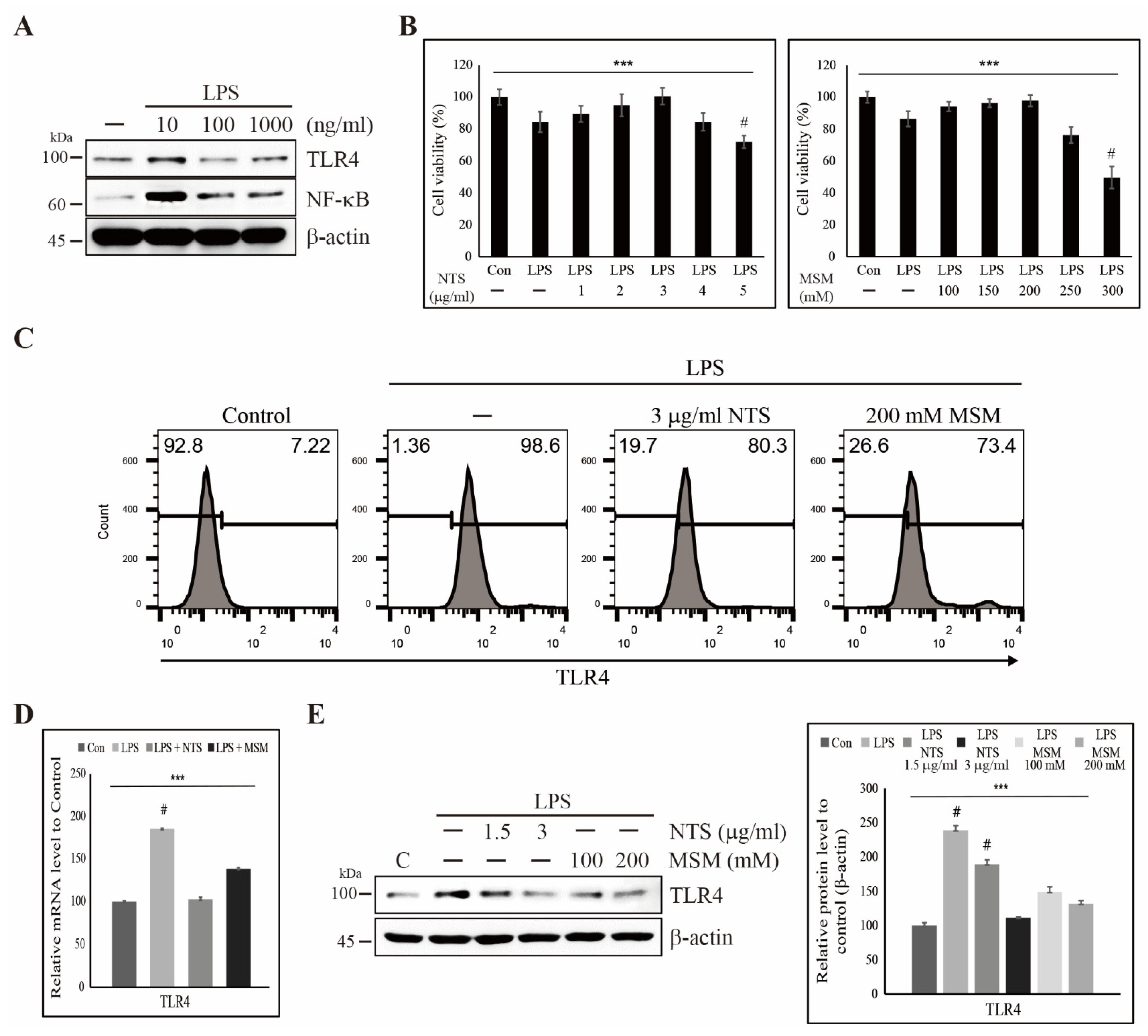
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts

The Ubiquitinated Axon: Local Control of Axon Development and Function by Ubiquitin | Journal of Neuroscience

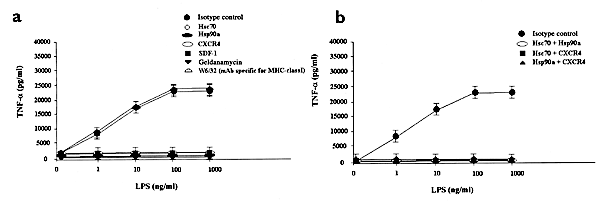
PDF) Acute-Phase Concentrations of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Binding Protein Inhibit Innate Immune Cell Activation by Different LPS Chemotypes via Different Mechanisms
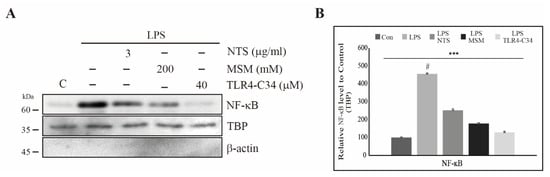
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts
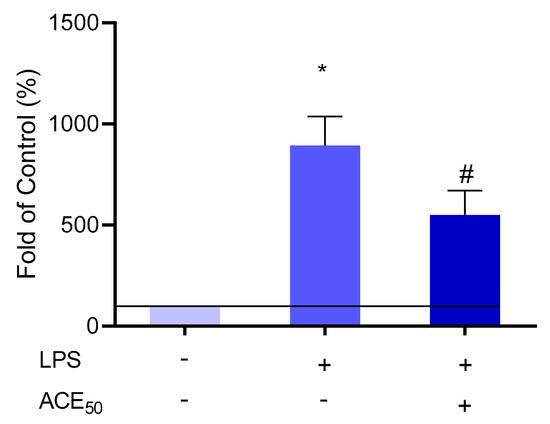
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Anthocyanin-Rich Sour Cherry Extract Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Inflammatory Response

PDF) Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts

LPS-induced expression and release of monocyte tissue factor in patients with haemophilia | SpringerLink
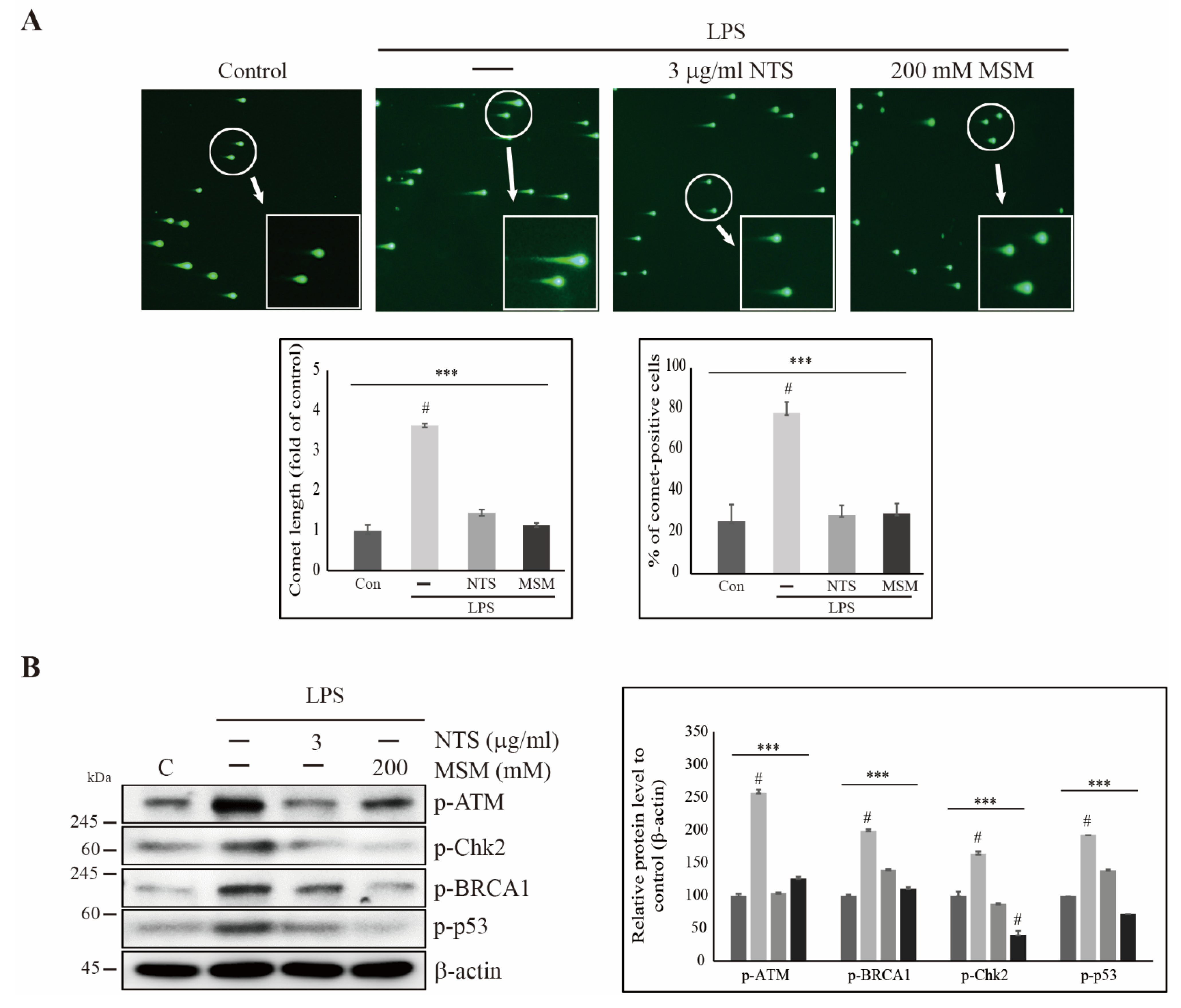
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts
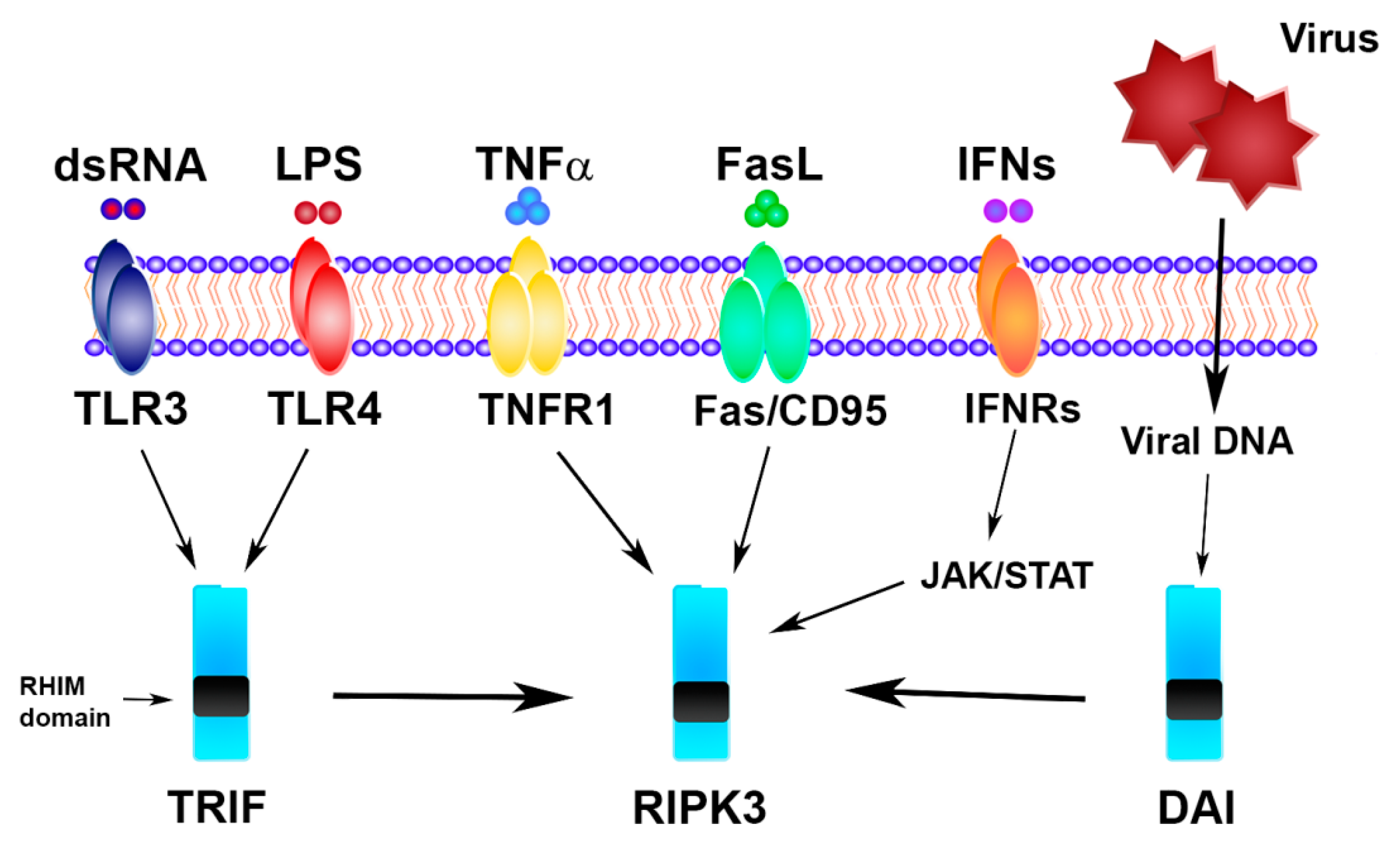
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | Necroptosis in Intestinal Inflammation and Cancer: New Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives

Molecules | Free Full-Text | Anthocyanin-Rich Sour Cherry Extract Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Inflammatory Response

Molecules | Free Full-Text | Anthocyanin-Rich Sour Cherry Extract Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Inflammatory Response
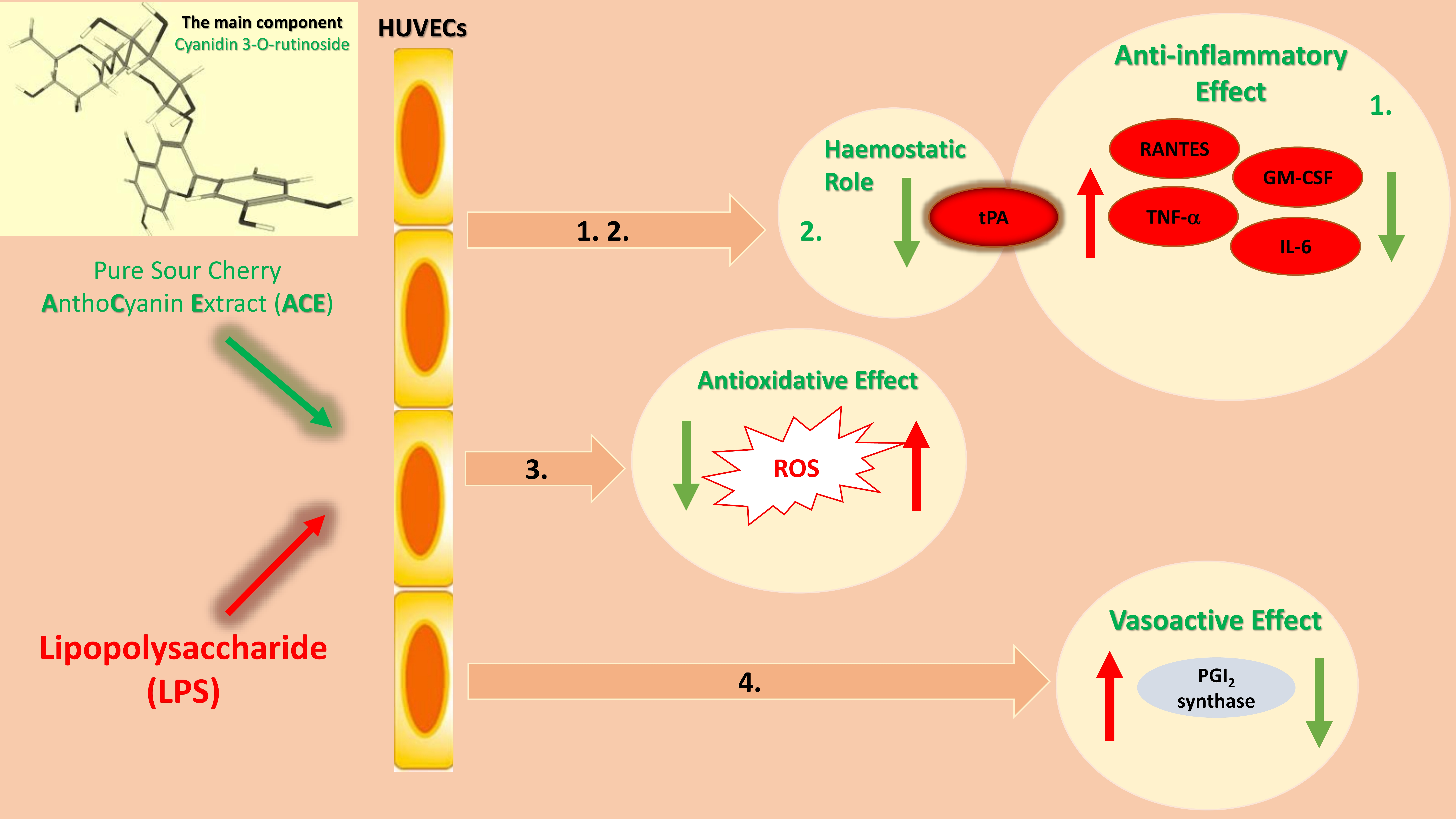
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Anthocyanin-Rich Sour Cherry Extract Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endothelial Inflammatory Response
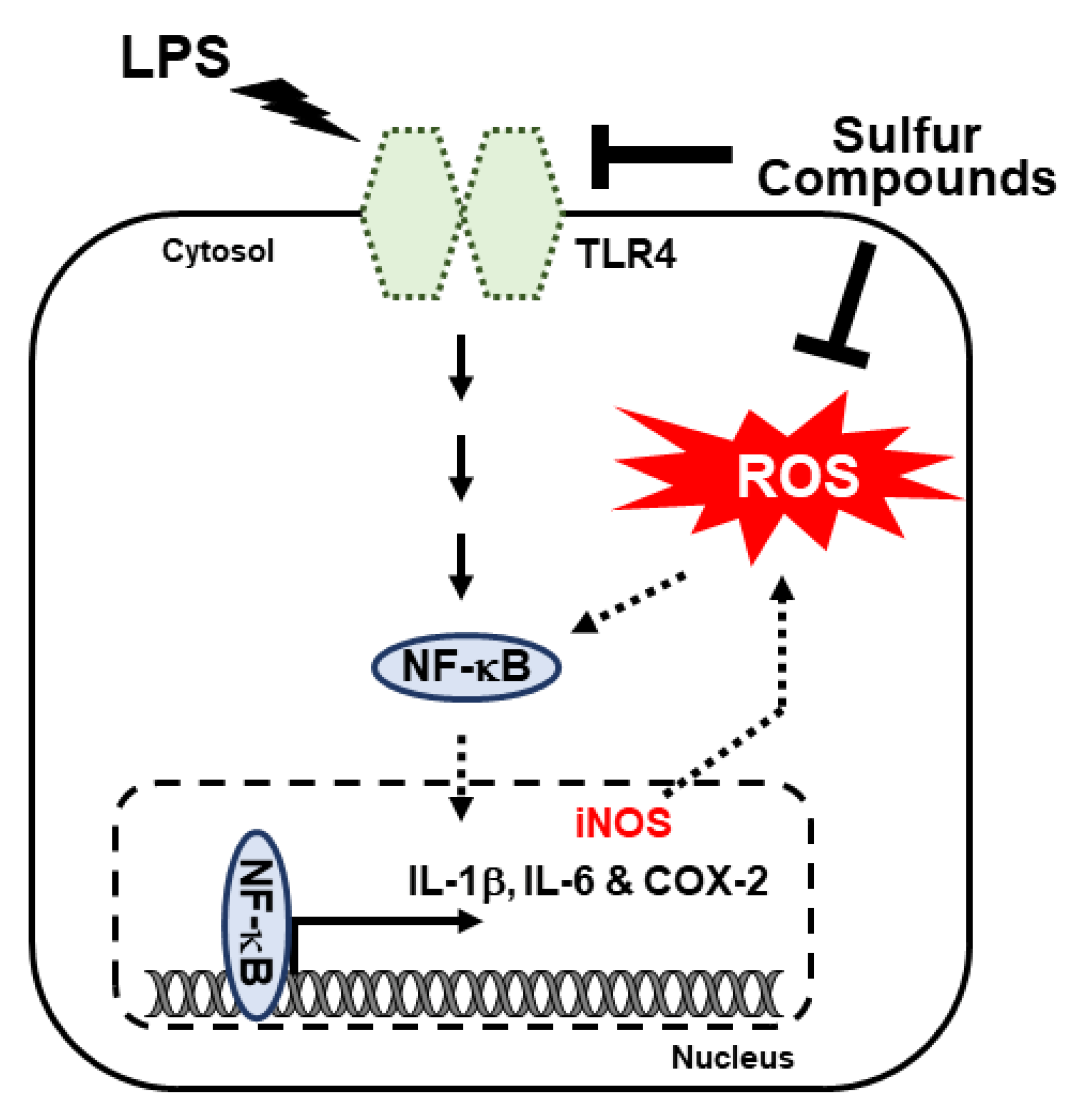
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts
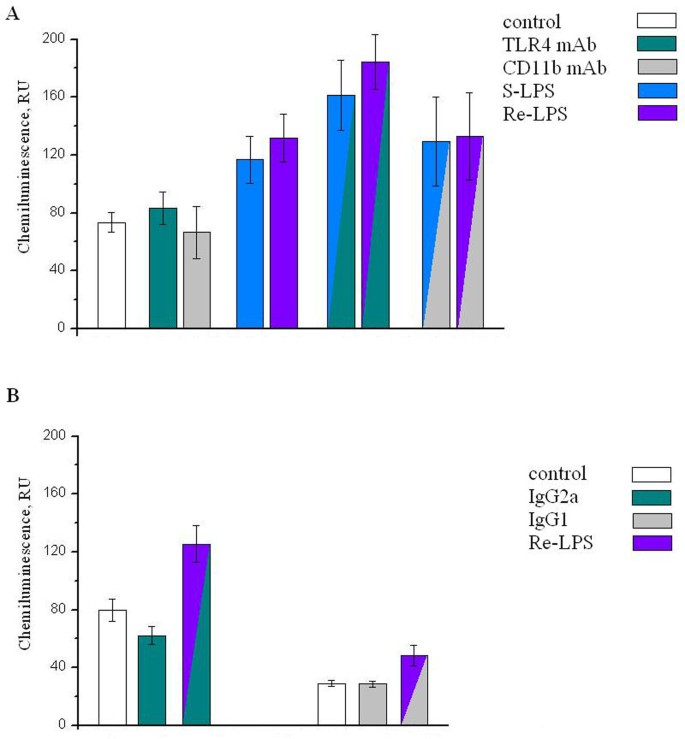
CD11b and TLR4 in human neutrophil priming by endotoxins from Escherichia coli | Critical Care | Full Text
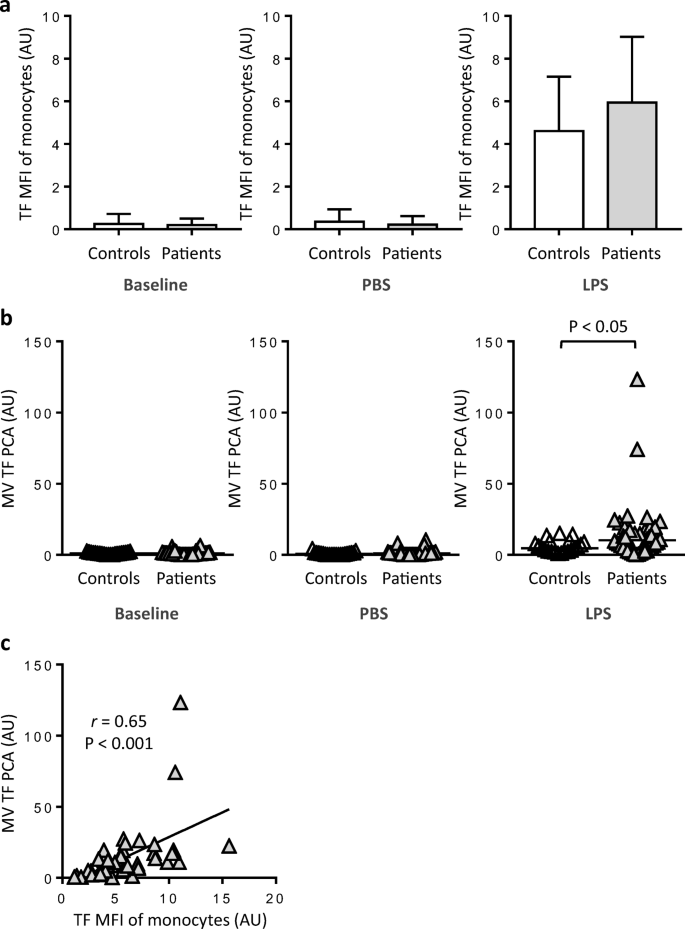
LPS-induced expression and release of monocyte tissue factor in patients with haemophilia | SpringerLink